Editor’s Note: This article originally appeared at Inside Climate News, a nonprofit, independent news organization that covers climate, energy, and the environment. It is republished with permission. Sign up for their newsletter here.
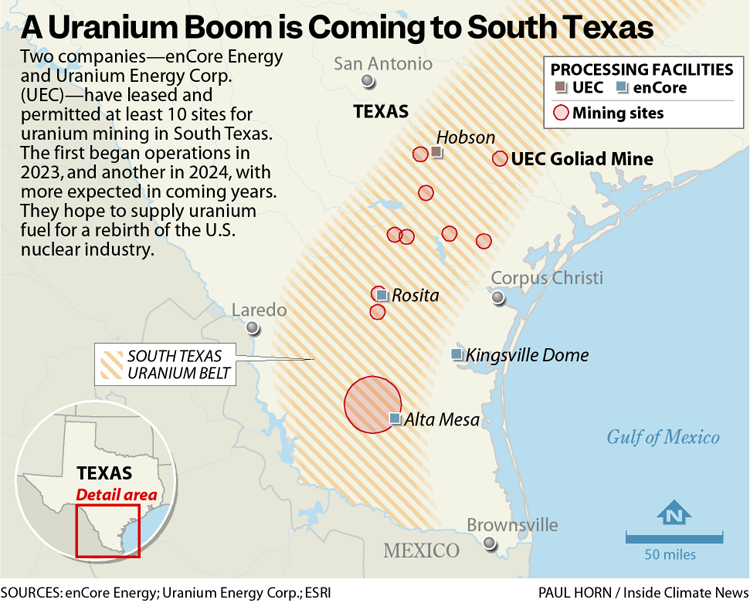
In the old ranchlands of South Texas, dormant uranium mines are coming back online. A collection of new ones hope to start production soon, extracting radioactive fuel from the region’s shallow aquifers. Many more may follow.
These mines are the leading edge of what government and industry leaders in Texas hope will be a nuclear renaissance, as America’s latent nuclear sector begins to stir again.
Texas is currently developing a host of high-tech industries that require enormous amounts of electricity, from crypto-currency mines and artificial intelligence to hydrogen production and seawater desalination. Now, powerful interests in the state are pushing to power it with next-generation nuclear reactors.
“We can make Texas the nuclear capital of the world,” said Reed Clay, president of the Texas Nuclear Alliance, former chief operating officer for Texas Gov. Greg Abbott’s office and former senior counsel to the Texas Office of Attorney General. “There’s a huge opportunity.”
Clay owns a lobbying firm with heavyweight clients that include SpaceX, Dow Chemical and the Texas Blockchain Council, among many others. He launched the Texas Nuclear Alliance in 2022 and formed the Texas Nuclear Caucus during the 2023 state legislative session to advance bills supportive of the nuclear industry.
The efforts come amid a national resurgence of interest in nuclear power, which can provide large amounts of energy without the carbon emissions that warm the planet. And it can do so with reliable consistency that wind and solar power generation lack. But it carries a small risk of catastrophic failure and requires uranium from mines that can threaten rural aquifers.
In South Texas, groundwater management officials have fought for almost 15 years against a planned uranium mine. Administrative law judges have ruled in their favor twice, finding potential for groundwater contamination. But in both cases those judges were overruled by the state’s main environmental regulator, the Texas Commission on Environmental Quality.
Now local leaders fear mining at the site appears poised to begin soon as momentum gathers behind America’s nuclear resurgence.
In October, Google announced the purchase of six small nuclear reactors to power its data centers by 2035. Amazon did the same shortly thereafter, and Microsoft has said it will pay to restart the Three Mile Island plant in Pennsylvania to power its facilities. Last month, President Joe Biden announced a goal to triple U.S. nuclear capacity by 2050. American companies are racing to license and manufacture new models of nuclear reactors.
“It’s kind of an unprecedented time in nuclear,” said James Walker, a nuclear physicist and co-founder of New York-based NANO Nuclear Energy Inc., a startup developing small-scale “microreactors” for commercial deployment around 2031.
The industry’s re-emergence stems from two main causes, he said: towering tech industry energy demands and the war in Ukraine.
Previously, the U.S. relied on enriched uranium from decommissioned Russian weapons to fuel its existing power plants and military vessels. When war interrupted that supply in 2022, American authorities urgently began to rekindle domestic uranium mining and enrichment.
“The Department of Energy at the moment is trying to build back a lot of the infrastructure that atrophied,” Walker said. “A lot of those uranium deposits in Texas have become very economical, which means a lot of investment will go back into those sites.”
In May, the White House created a working group to develop guidelines for deployment of new nuclear power projects. In June, the Department of Energy announced $900 million in funding for small, next-generation reactors. And in September, it announced a $1.5 billion loan to restart a nuclear power plant in Michigan, which it called “a first of a kind effort.”
“There’s an urgent desire to find zero-carbon energy sources that aren’t intermittent like renewables,” said Colin Leyden, Texas state director of the Environmental Defense Fund. “There aren’t a lot of options, and nuclear is one.”
Wind and solar will remain the cheapest energy sources, Leyden said, and a buildout of nuclear power would likely accelerate the retirement of coal plants.
The U.S. hasn’t built a nuclear reactor in 30 years, spooked by a handful of disasters. In contrast, China has grown its nuclear power generation capacity almost 900 percent in the last 20 years, according to the World Nuclear Association, and currently has 30 reactors under construction.
Last year, Abbott ordered the state’s Public Utility Commission to produce a report “outlining how Texas will become the national leader in using advanced nuclear energy.” According to the report, which was issued in November, new nuclear reactors would most likely be built in ports and industrial complexes to power large industrial operations and enable further expansion.
“The Ports and their associated industries, like Liquified Natural Gas (LNG), carbon capture facilities, hydrogen facilities and cruise terminals, need additional generation sources,” the report said. Advanced nuclear reactors “offer Texas’ Ports a unique opportunity to enable continued growth.”
In the Permian Basin, the report said, reactors could power oil production as well as purification of oilfield wastewater “for useful purposes.” Or they could power clusters of data centers in Central and North Texas.
Already, Dow Chemical has announced plans to install four small reactors at its Seadrift plastics and chemical plant on a rural stretch of the middle Texas coast, which it calls the first grid-scale nuclear reactor for an industrial site in North America.
“I think the vast majority of these nuclear power plants are going to be for things like industrial use,” said Cyrus Reed, a longtime environmental lobbyist in the Texas Capitol and conservation director for the state’s Sierra Club chapter. “A lot of large industries have corporate goals of being low carbon or no carbon, so this could fill in a niche for them.”
The PUC report made seven recommendations for the creation of public entities, programs and funds to support the development of a Texas nuclear industry. During next year’s state legislative session, legislators in the Nuclear Caucus will seek to make them law.
“It’s going to be a great opportunity for energy investment in Texas,” said Stephen Perkins, Texas-based chief operating officer of the American Conservation Coalition, a conservative environmental policy group. “We’re really going to be pushing hard for [state legislators] to take that seriously.”
However, Texas won’t likely see its first new commercial reactor come online for at least five years. Before a buildout of power plants, there will be a boom at the uranium mines, as the U.S. seeks to reestablish domestic production and enrichment of uranium for nuclear fuel.
Ted Long, a former commissioner of Goliad County, can see the power lines of an inactive uranium mine from his porch on an old family ranch in the rolling golden savannah of South Texas. For years the mine has been idle, waiting for depressed uranium markets to pick up.
There, an international mining company called Uranium Energy Corp. plans to mine 420 acres of the Evangeline Aquifer between depths of 45 and 404 feet, according to permitting documents. Long, a dealer of engine lubricants, gets his water from a well 120 feet deep that was drilled in 1993. He lives with his wife on property that’s been in her family since her great-grandfather emigrated from Germany.
“I’m worried for groundwater on this whole Gulf Coast,” Long said. “This isn’t the only place they’re wanting to do this.”
As a public official, Long fought the neighboring mine for years. But he found the process of engaging with Texas’ environmental regulator, the Texas Commission on Environmental Quality, to be time-consuming, expensive and ultimately fruitless. Eventually, he concluded there was no point.
“There’s nothing I can do,” he said. “I guess I’ll have to look for some kind of system to clean the water up.”
The Goliad mine is the smallest of five sites in South Texas held by UEC, which is based in Corpus Christi. Another company, enCore Energy, started uranium production at two South Texas sites in 2023 and 2024, and hopes to bring four more online by 2027.
Uranium mining goes back decades in South Texas, but lately it’s been dormant. Between the 1970s and the 1990s, a cluster of open pit mines harvested shallow uranium deposits at the surface. Many of those sites left a legacy of aquifer pollution.
TCEQ records show active cases of groundwater contaminated with uranium, radium, arsenic and other pollutants from defunct uranium mines and tailing impoundment sites in Live Oak County at ExxonMobil’s Ray Point site, and in Karnes County at Conoco-Phillips Co.’s Conquista Project and at Rio Grande Resources’ Panna Maria Uranium Recovery Facility.
All known shallow deposits of uranium in Texas have been mined. The deeper deposits aren’t accessed by traditional surface mining, but rather a process called in-situ mining, in which solvents are pumped underground into uranium-bearing aquifer formations. Adjacent wells suck back up the resulting slurry, from which uranium dust will be extracted.
Industry describes in-situ mining as safer and more environmentally friendly than surface mining. But some South Texas water managers and landowners are concerned.
“We’re talking about mining at the same elevation as people get their groundwater,” said Terrell Graham, a board member of the Goliad County Groundwater Conservation District, which has been fighting a proposed uranium mine for almost 15 years. “There isn’t another source of water for these residents.”
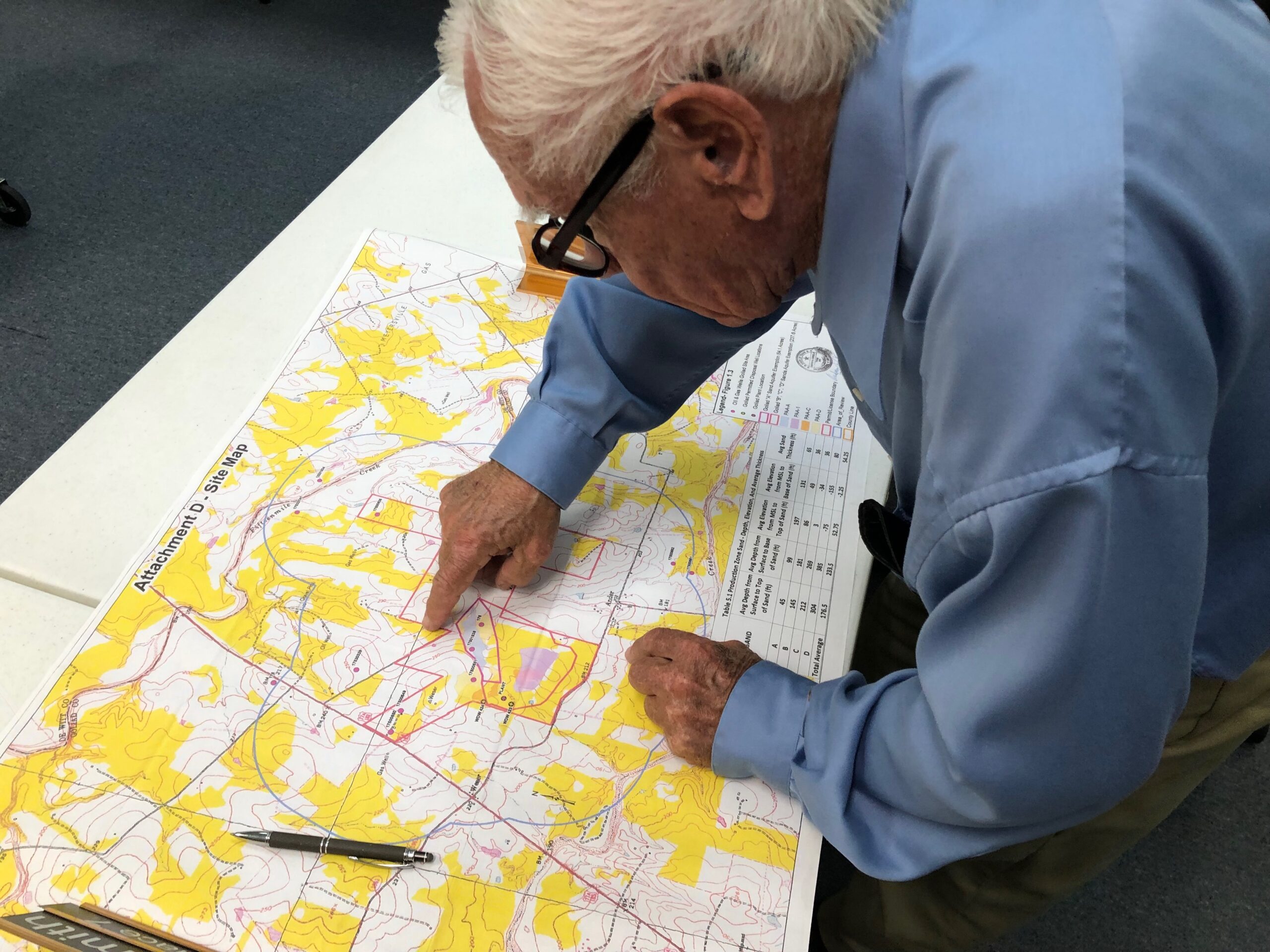
On two occasions, the district has participated in lengthy hearings and won favorable rulings in Texas’ administrative courts supporting concerns over the safety of the permits. But both times, political appointees at the TCEQ rejected judges’ recommendations and issued the permits anyway.
“We’ve won two administrative proceedings,” Graham said. “It’s very expensive, and to have the TCEQ commissioners just overturn the decision seems nonsensical.”
The first time was in 2010. UEC was seeking initial permits for the Goliad mine, and the groundwater conservation district filed a technical challenge claiming that permits risked contamination of nearby aquifers.
The district hired lawyers and geological experts for a three-day hearing on the permit in Austin. Afterwards, an administrative law judge agreed with some of the district’s concerns. In a 147-page opinion issued September 2010, an administrative law judge recommended further geological testing to determine whether certain underground faults could transmit fluids from the mining site into nearby drinking water sources.
“If the Commission determines that such remand is not feasible or desirable then the ALJ recommends that the Mine Application and the PAA-1 Application be denied,” the opinion said.
But the commissioners declined the judge’s recommendation. In an order issued March 2011, they determined that the proposed permits “impose terms and conditions reasonably necessary to protect fresh water from pollution.”
“The Commission determines that no remand is necessary,” the order said.
The TCEQ issued UEC’s permits, valid for 10 years. But by that time, a collapse in uranium prices had brought the sector to a standstill, so mining never commenced.
In 2021, the permits came up for renewal, and locals filed challenges again. But again, the same thing happened.
A nearby landowner named David Michaelsen organized a group of neighbors to hire a lawyer and challenge UEC’s permit to inject the radioactive waste product from its mine more than half a mile underground for permanent disposal.
“It’s not like I’m against industry or anything, but I don’t think this is a very safe spot,” said Michaelsen, former chief engineer at the Port of Corpus Christi, a heavy industrial hub on the South Texas Coast. He bought his 56 acres in Goliad County in 2018 to build an upscale ranch house and retire with his wife.
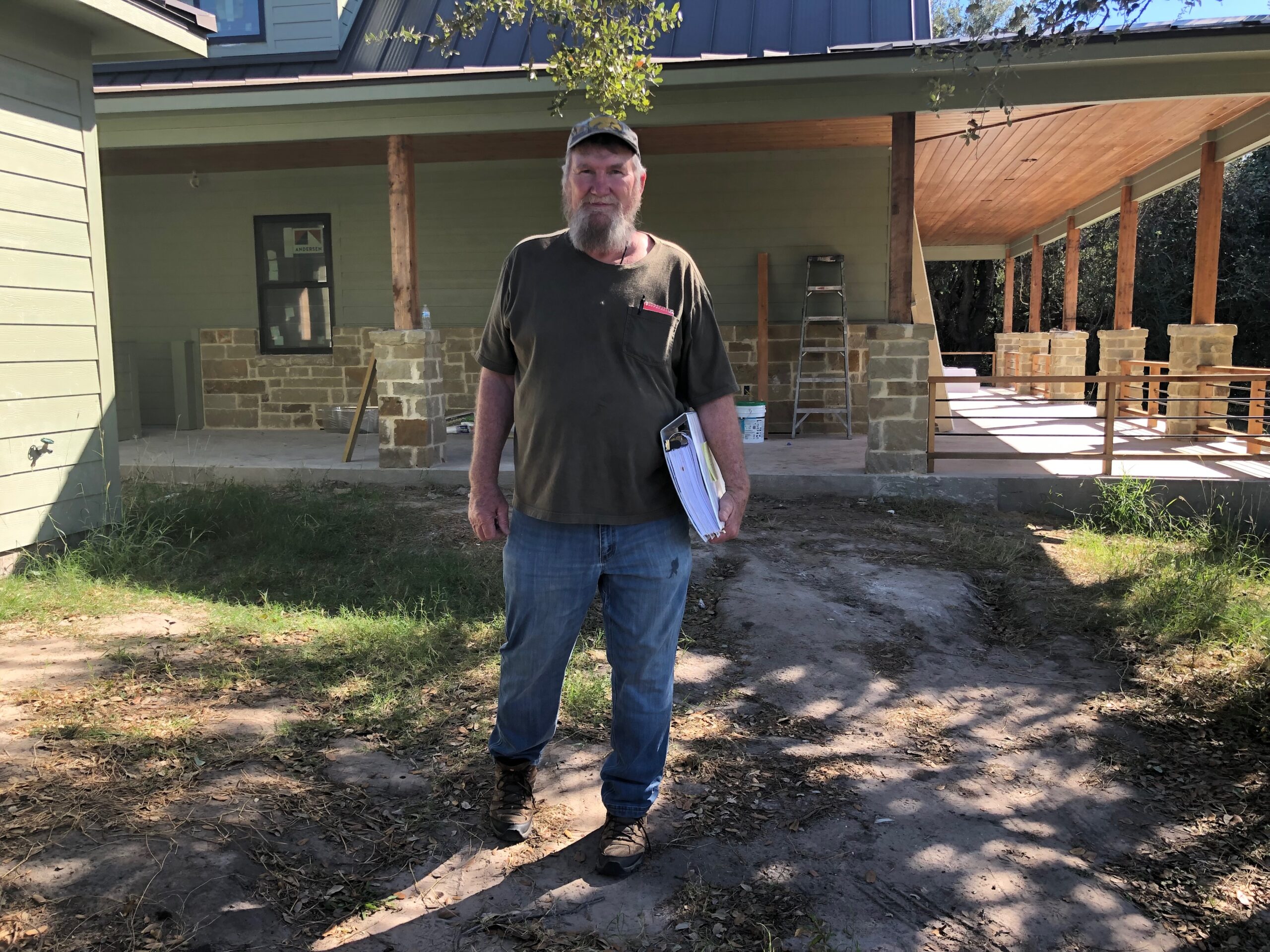

In hearings before an administrative law judge, he presented evidence showing that nearby faults and old oil well shafts posed a risk for the injected waste to travel into potable groundwater layers near the surface.
In a 103-page opinion issued April 2024, an administrative law judge agreed with many of Michaelsen’s challenges, including that “site-specific evidence here shows the potential for fluid movement from the injection zone.”
“The draft permit does not comply with applicable statutory and regulatory requirements,” wrote the administrative law judge, Katerina DeAngelo, a former assistant attorney general of Texas in the environmental protection division. She recommended “closer inspection of the local geology, more precise calculations of the [cone of influence], and a better assessment of the faults.”
Michaelsen thought he had won. But when the TCEQ commissioners took up the question several months later, again they rejected all of the judge’s findings.
In a 19-page order issued in September, the commission concluded that “faults within 2.5 miles of its proposed disposal wells are not sufficiently transmissive or vertically extensive to allow migration of hazardous constituents out of the injection zone.” The old nearby oil wells, the commission found, “are likely adequately plugged and will not provide a pathway for fluid movement.”
“UEC demonstrated the proposed disposal wells will prevent movement of fluids that would result in pollution” of an underground source of drinking water, said the order granting the injection disposal permits.
“I felt like it was rigged, a setup,” said Michaelsen, holding his four-inch-thick binder of research and records from the case. “It was a canned decision.”
Another set of permit renewals remains before the Goliad mine can begin operation, and local authorities are fighting it, too. In August, the Goliad County Commissioners Court passed a resolution against uranium mining in the county. The groundwater district is seeking to challenge the permits again in administrative court. And in November, the district sued TCEQ in Travis County District Court seeking to reverse the agency’s permit approvals.
Because of the lawsuit, a TCEQ spokesperson declined to answer questions about the Goliad County mine site, saying the agency doesn’t comment on pending litigation.
A final set of permits remains to be renewed before the mine can begin production. However, after years of frustrations, district leaders aren’t optimistic about their ability to influence the decision.
Only about 40 residences immediately surround the site of the Goliad mine, according to Art Dohmann, vice president of the Goliad County Groundwater Conservation District. Only they might be affected in the near term. But Dohmann, who has served on the groundwater district board for 23 years, worries that the uranium, radium and arsenic churned up in the mining process will drift from the site as years go by.
“The groundwater moves. It’s a slow rate, but once that arsenic is liberated, it’s there forever,” Dohmann said. “In a generation, it’s going to affect the downstream areas.”
UEC did not respond to a request for comment.
Currently, the TCEQ is evaluating possibilities for expanding and incentivizing further uranium production in Texas. It’s following instruction given last year, when lawmakers with the Nuclear Caucus added an item to TCEQ’s bi-annual budget ordering a study of uranium resources to be produced for state lawmakers by December 2024, ahead of next year’s legislative session.
According to the budget item, “The report must include recommendations for legislative or regulatory changes and potential economic incentive programs to support the uranium mining industry in this state.”
A major push is underway to revive the American nuclear industry, promising huge amounts of energy without carbon emissions that warm the planet. But nearby nascent uranium mines, landowners fear for their groundwater.
The U.S. hasn’t built a nuclear reactor in 30 years. Meanwhile China has grown its nuclear power generation capacity by 900% and currently has 30 reactors under construction.
The US is gunning for a nuclear renaissance to meet the enormous energy demands of next-generation industry like artificial intelligence, cryptocurrency and data centers
In the old ranch lands of South Texas, dormant uranium mines are coming back online. State and industry leaders say it’s the leading edge of a national nuclear renaissance, but rural landowners fear groundwater contamination.
Groundwater management officials in Goliad County have been fighting a planned uranium mine for years. But they’ve never won the sympathy of Texas’ environmental regulator.
(Except for the headline, this story has not been edited by PostX News and is published from a syndicated feed.)