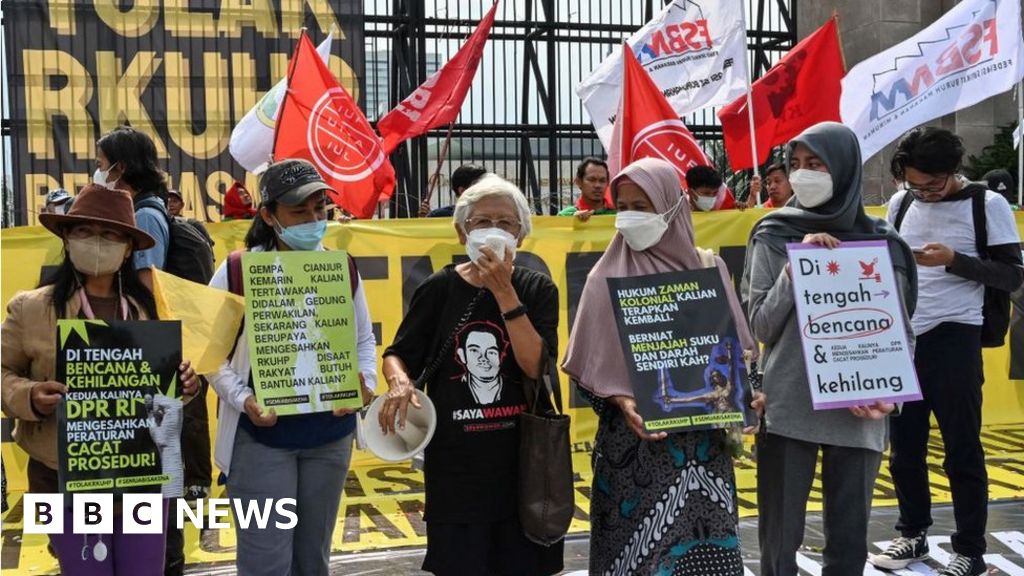
Indonesia is not a secular state. Atheism is unacceptable – technically you need to follow one of five prescribed religions. So it is a multi-religious state with an official ideology, Pancasila, which prioritises no faith over any other. That was Indonesia’s post-independence leader Sukarno’s idea, to discourage large parts of the archipelago where Muslims are not a majority from breaking away.But since the fall of Suharto – who ruthlessly suppressed political Islamic groups – there has been growing mobilisation around Islamic values, the sense that Islam is threatened by outside influences and more conservatism in many areas of the island of Java, where more than half of Indonesians live. Political parties have responded to this and demanded tougher laws to police morals. Current leader Jokowi is from the syncretic Javanese tradition that adheres to a more flexible form of Islam, but his main preoccupation is his legacy of economic development rather than tolerance and liberal values. He has shown, for example in the jailing of former Jakarta governor Ahok on blasphemy charges, that he’s willing to give hardline Muslims some of what they want.
(Except for the headline, this story has not been edited by PostX News and is published from a syndicated feed.)